 |
 |
|
|
Background
Two bandwidth metrics that are commonly associated with a path are the capacity and the available bandwidth. The capacity is the maximum throughput that the path can provide to an application when there is no competing traffic load (cross traffic). The available bandwidth, on the other hand, is the maximum throughput that the path can provide to an application, given the path's current cross traffic load. Our main objective is to develop methodologies and tools that can accurately measure these two bandwidth metrics. Measuring the capacity is crucial for `debugging', calibrating, and managing a path. Measuring the available bandwidth, on the other hand, is of great importance for predicting the end-to-end performance of applications, for dynamic path selection and traffic engineering, and for selecting between a number of differentiated classes of service. Additional constraints about these measurement methodologies are that they should not have a negative impact on the normal network traffic (i.e., non-intrusive methods), they can be performed in real-time, and they should not require information from the path routers.
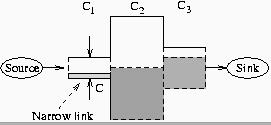
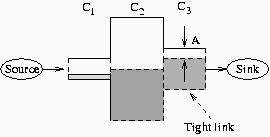
Figure 1
TOP: The capacity of a path is determined by the link with the minimum capacity (narrow link). In this example, the capacity is C=C1.
DOWN: The available bandwidth of a path is determined by the link with the minimum unused capacity (tight link). In this example, the available bandwidth is the part of the tight link that is shown as A.
People
Funding for the BW-meter project has been provided by
the following two grants:
CAREER: Putting Measurements to Work: Design and Evaluation of
Measurement-Driven Network Mechanisms of the
US National Science Foundation,
and by the
Scientific Discovery through Advanced Computing (SciDAC) program, of the
US Department of Energy (Office of Science).
Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations
expressed in this material are those of the authors and do
not necessarily reflect the views of NSF or DOE.
See also our
bandwidth estimation project web page,
maintained at CAIDA.