Georgia Tech Researchers Awarded $7.5 Million from Office of Naval Research for Secure Stack
A team of Georgia Tech researchers from the School of Computer Science (SCS) has been awarded $7.5 million from the Office of Naval Research to develop a customized attack-resistant software stack.
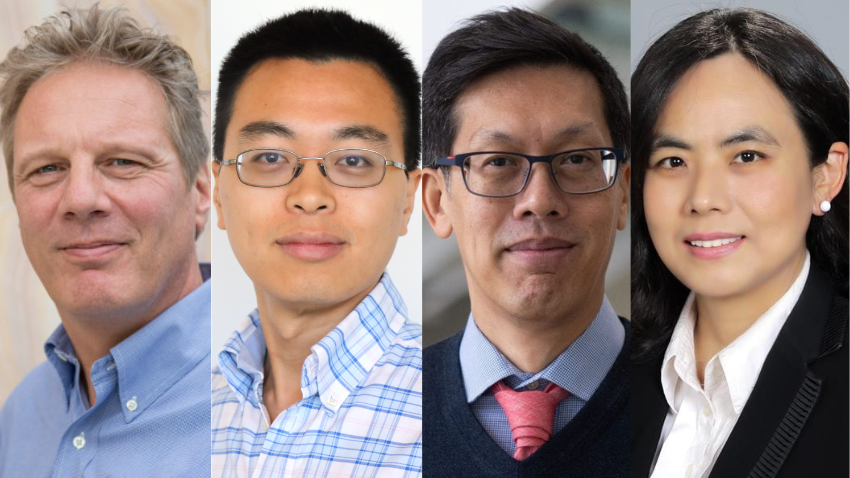
SCS Assistant Professor Bill Harris is the principal investigator on the project and is collaborating with Professors Wenke Lee and Alessandro Orso, Associate Professor Santosh Pande, and Assistant Professor Taesoo Kim.
The researchers are working on a technique for reducing what’s known as the attack surface, the total number of ways in which a program can be vulnerable to exploit. Most general-purpose software includes code that not every user needs and unused code can create exploit opportunities for attackers. Through this research, users will be able to run software in which unneeded code is removed, thus decreasing the vulnerability of the programs they use.
Lee compares the project to a house. “When you build a house, you only really need one door, but the house may still have multiple doors. The number of doors increases the opportunity to break in,” Lee said. “If you only have one door, your house is more secure.”
In order to do this, the researchers are looking at the full stack of software systems, including applications, operating systems, and possibly Internet of Things devices. They are planning to use static and dynamic analysis techniques to determine which pathways through the system different users need. Each researcher has a specific area of expertise:
- Pande’s focus on compilers will help determine what essential code must be loaded for each user during application execution.
- Harris’s expertise with static analysis will provide guarantees that the software maintains its integrity despite removed code.
- Orso will use dynamic analysis and testing techniques to confirm the modified system still functions as expected.
- Kim will use his expertise in systems to determine which modules can be removed from the operating system without compromising its functionality.
- Lee will focus on the aspects related to security and use his expertise to analyze and experiment with malware.
Overall, the five researchers have the set of complementary skills needed for the project to be successful. Over the five-year life of the grant, the researchers expect to develop a series of approaches for reducing attack surface that anyone can use on complex systems, as well as on low-level code.
“Going back to the house metaphor, the problem is that different people want to use different doors,” Orso says. “Our research will allow users to customize the house for each person so that it contains only the door that person needs.”